How to Scan a QR Code on an iPhone or Android
These days, you can find QR codes on everything from candy wrappers to billboards. Scanning these modern-day barcodes with your smartphone lets you quickly open a web page, download an app, send a text message, and much more. Many restaurants and bars are even replacing their menus with QR codes, while some stores allow you to pay with a QR code now, so you don’t have to touch anything. Here’s how to scan a QR code with your iPhone or Android phone and what to do when you can’t scan them.

How to Scan a QR Code on an iPhone
To scan a QR code on your iPhone, all you have to do is open the Camera app and point your phone at the QR code. Make sure the QR code is inside the box on your screen, and then tap the pop-up banner or the yellow QR code icon in the bottom-right corner.
- Open the Camera app on your iPhone. You can quickly open the camera app by swiping left from the lock screen. Or you can swipe down from the middle of your home screen and type “Camera” into the search bar at the top of your screen.
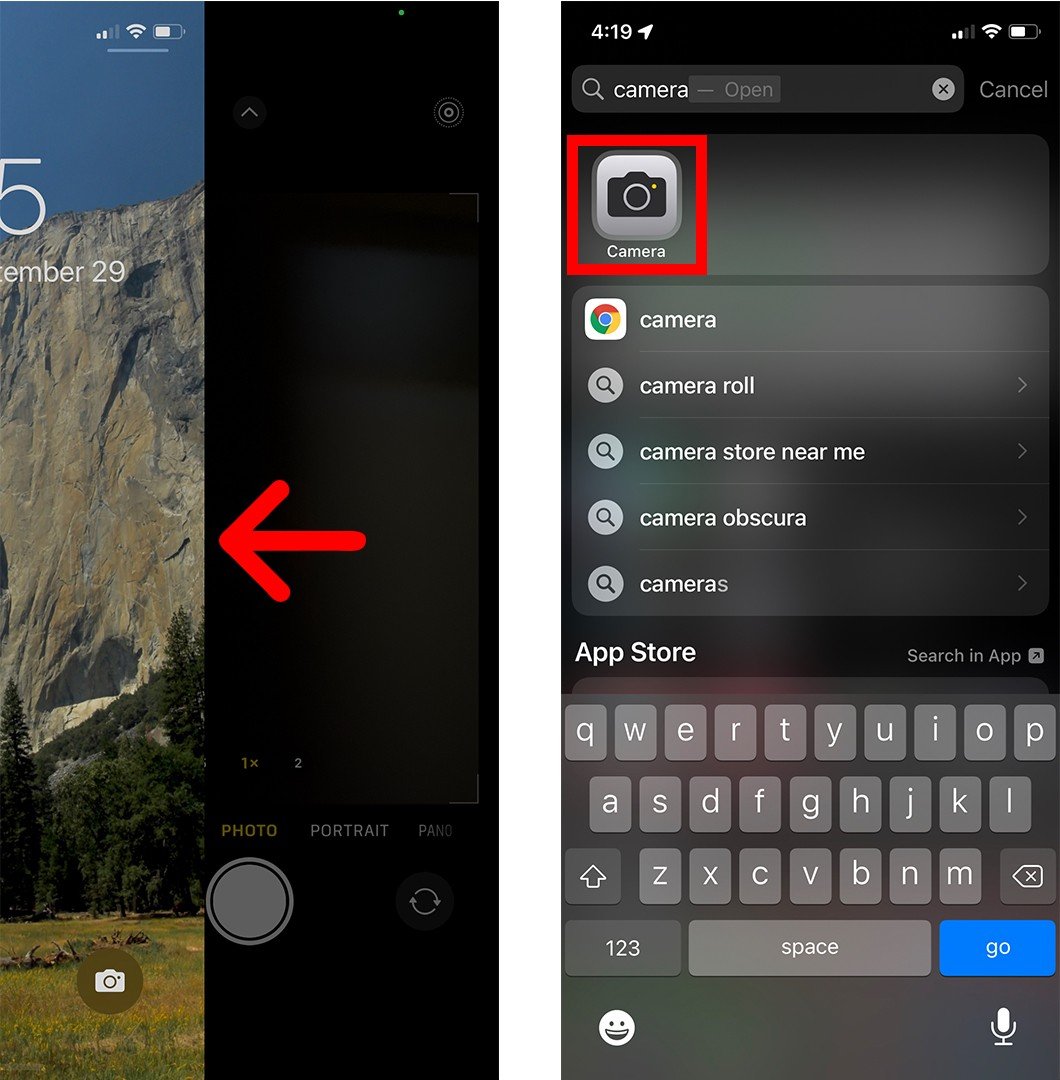
- Then point your iPhone at the QR code to scan it. You don’t have to fill the entire screen, but make sure that you can see all four corners of the QR code in the app. Once you correctly scan the QR code, a pop-up banner will appear above it, and you will also see a yellow QR code icon appear in the bottom right corner.
- Finally, tap the pop-up banner or the QR icon in the bottom-right corner of the app. This will immediately send you to the website, open the app, or perform another action, so make sure you know what the banner does before tapping on it.
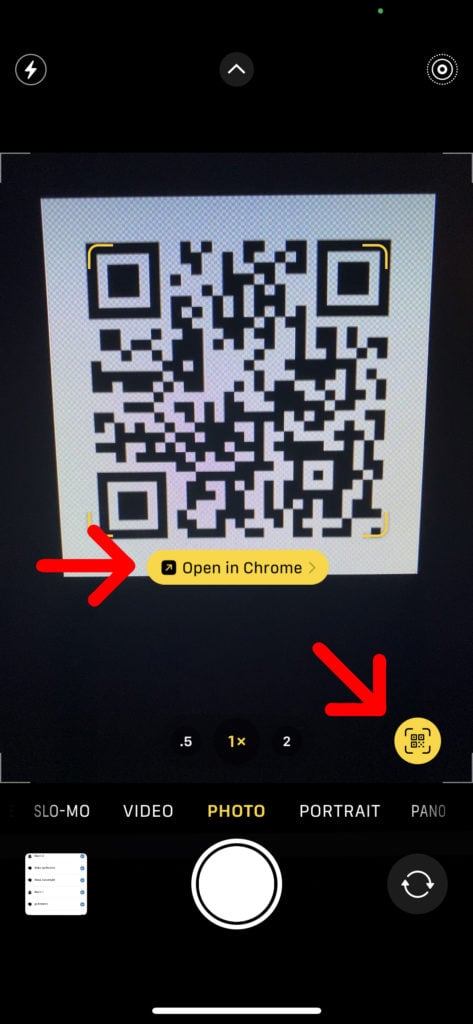
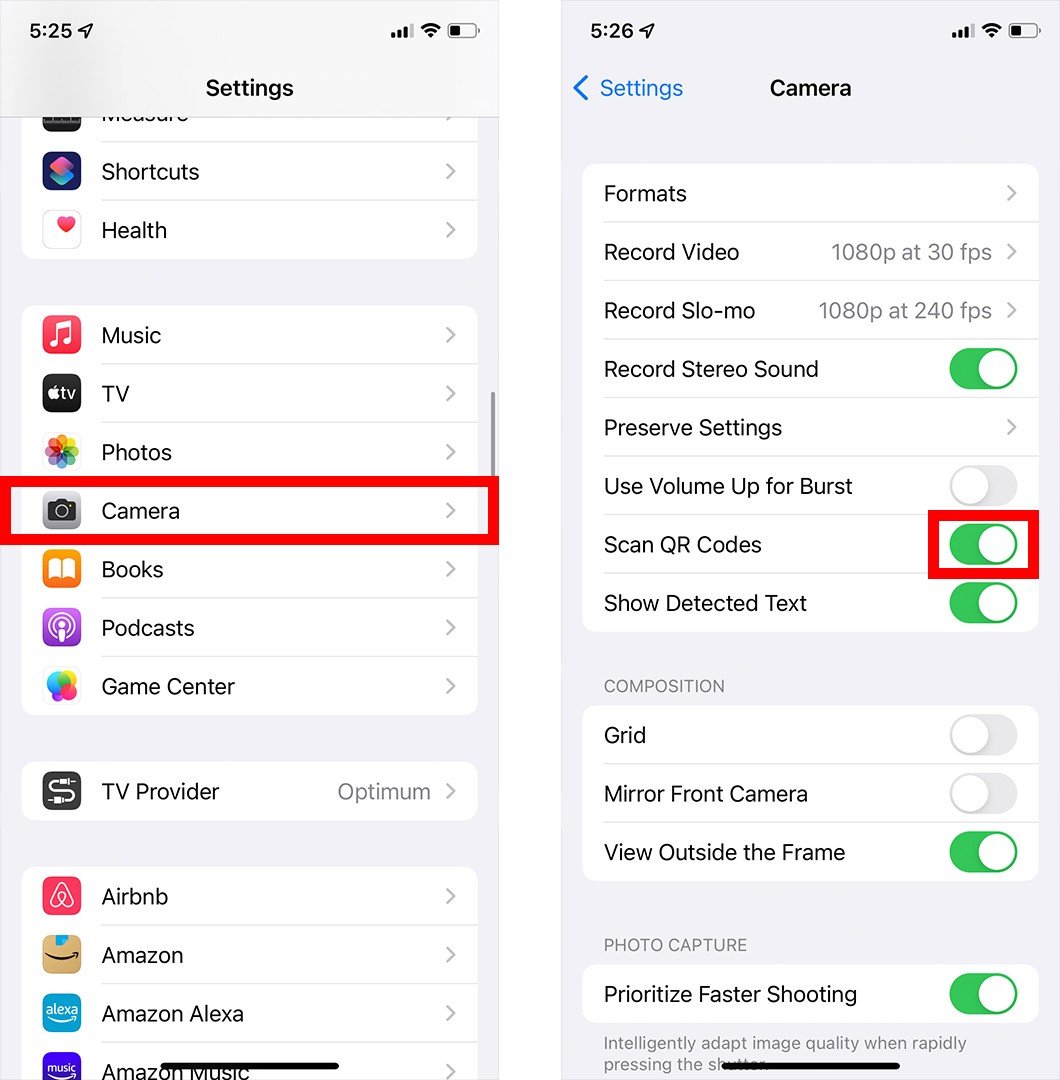
If you don’t see the banner or QR icon, make sure that you have the Scan QR Codes feature enabled. You can do this by going to Settings > Camera and tapping the slider next to Scan QR Codes. You will know it is turned on when it is green.
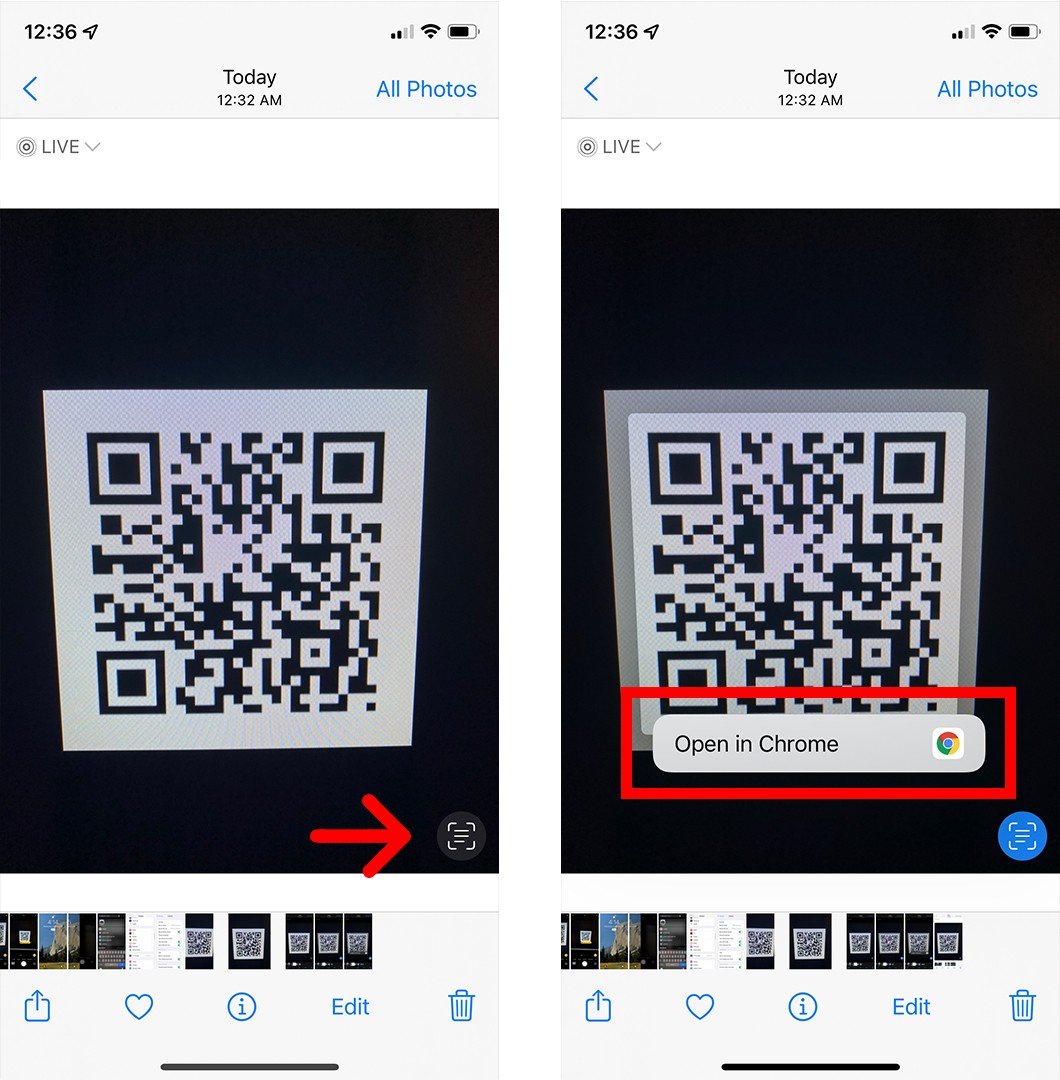
If you still don’t see the pop-up banner or QR code icon, take a picture of the QR code and open it in the Photos app. Then tap the Live Text icon that looks like three lines in a box in the bottom-right corner. Finally, tap the QR code, and then the pop-up banner should appear.
If you want to know more about how to take a screenshot on an iPhone, check out our step-by-step guide here.

How to Scan a QR code on an Android Phone
If you’re running Android 8 or later, you can scan a QR code by opening the camera app, pointing your phone at the QR code, and tapping the pop-up banner. If you don’t see the pop-up banner, you can use the Google Lens app to scan the QR code instead.
- Open the Camera app on your Android phone. You can open the camera app by swiping up from the bottom of your screen. Or you can tap the search bar on your home screen and enter “Camera.”
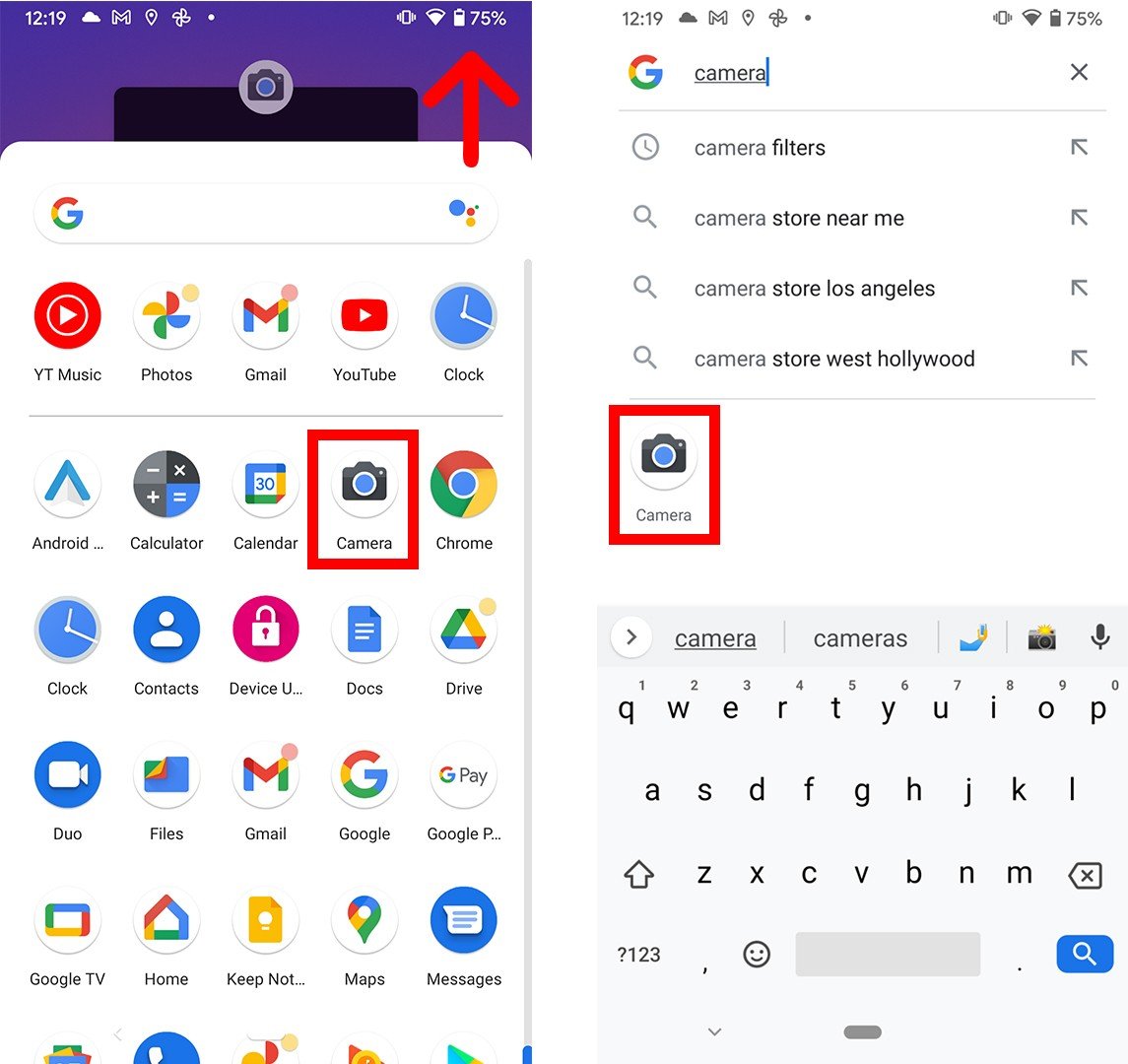
- Then point your Android phone at the QR code to scan it. Make sure that all four corners of the QR code are visible in the viewfinder. If you are running Android 8 or later, you should see a pop-up banner appear.
- Finally, tap the pop-up banner. This will immediately send you to the website, open the app, or perform another action, so make sure you know what the banner does before tapping on it.
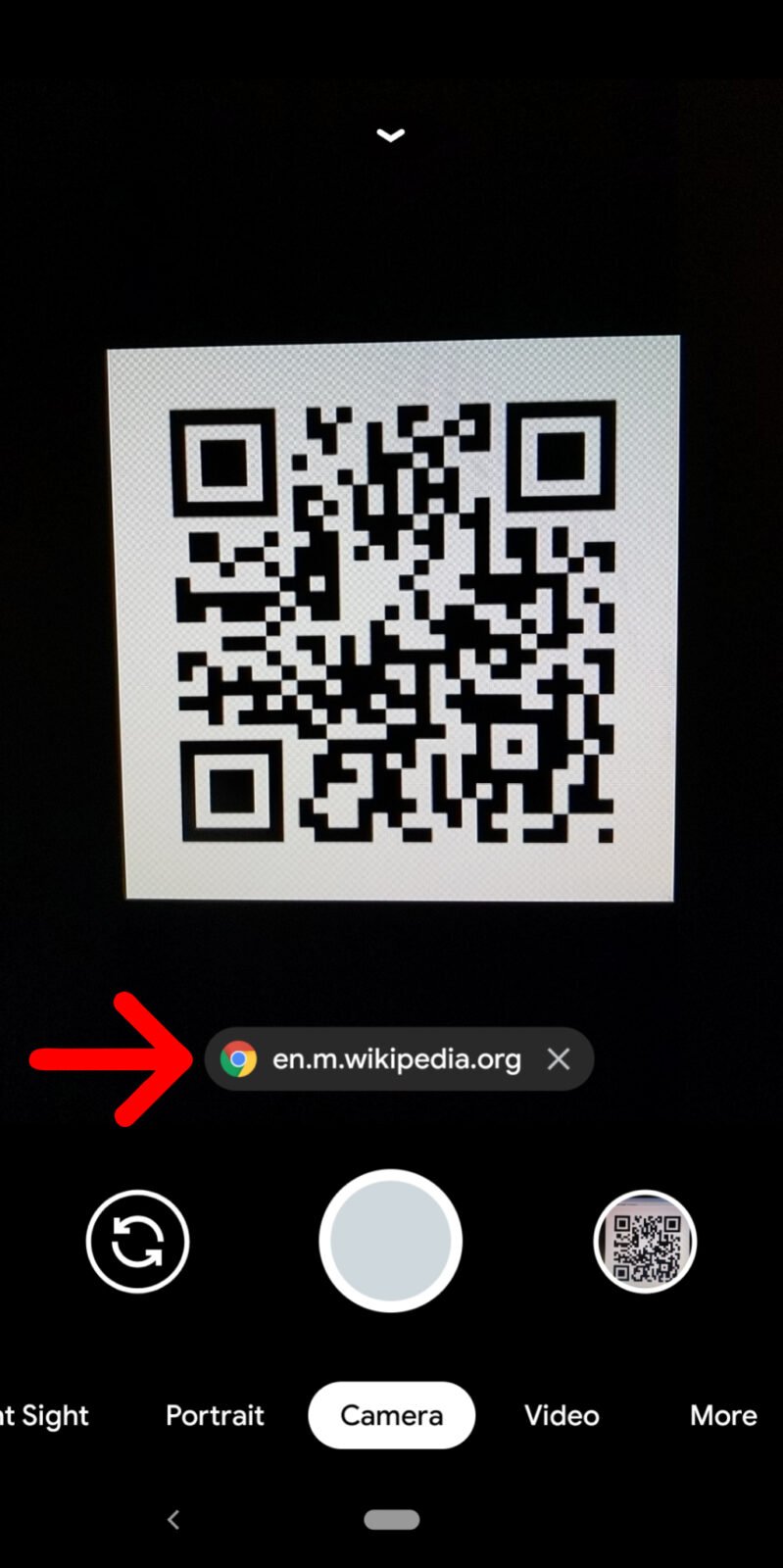
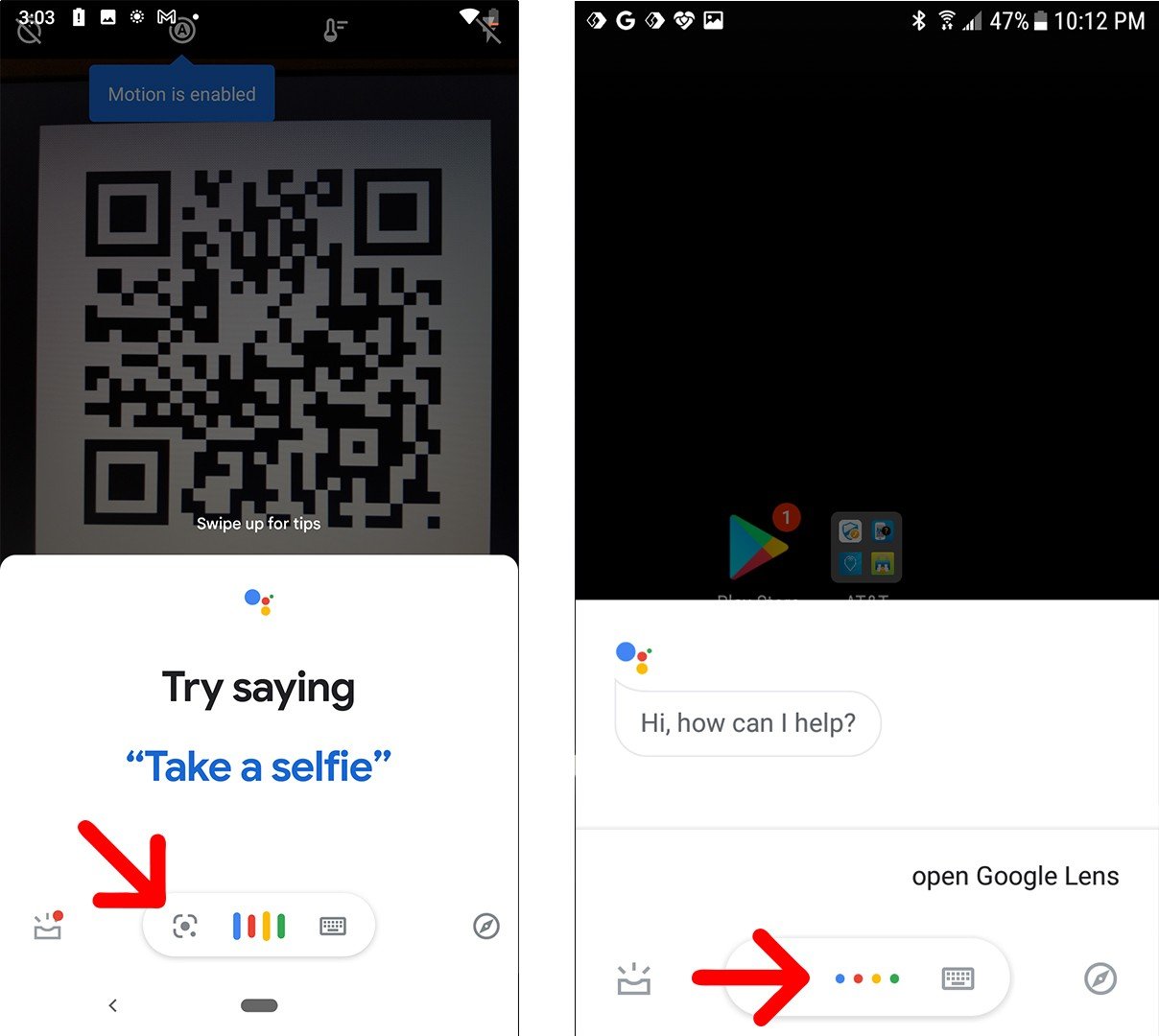
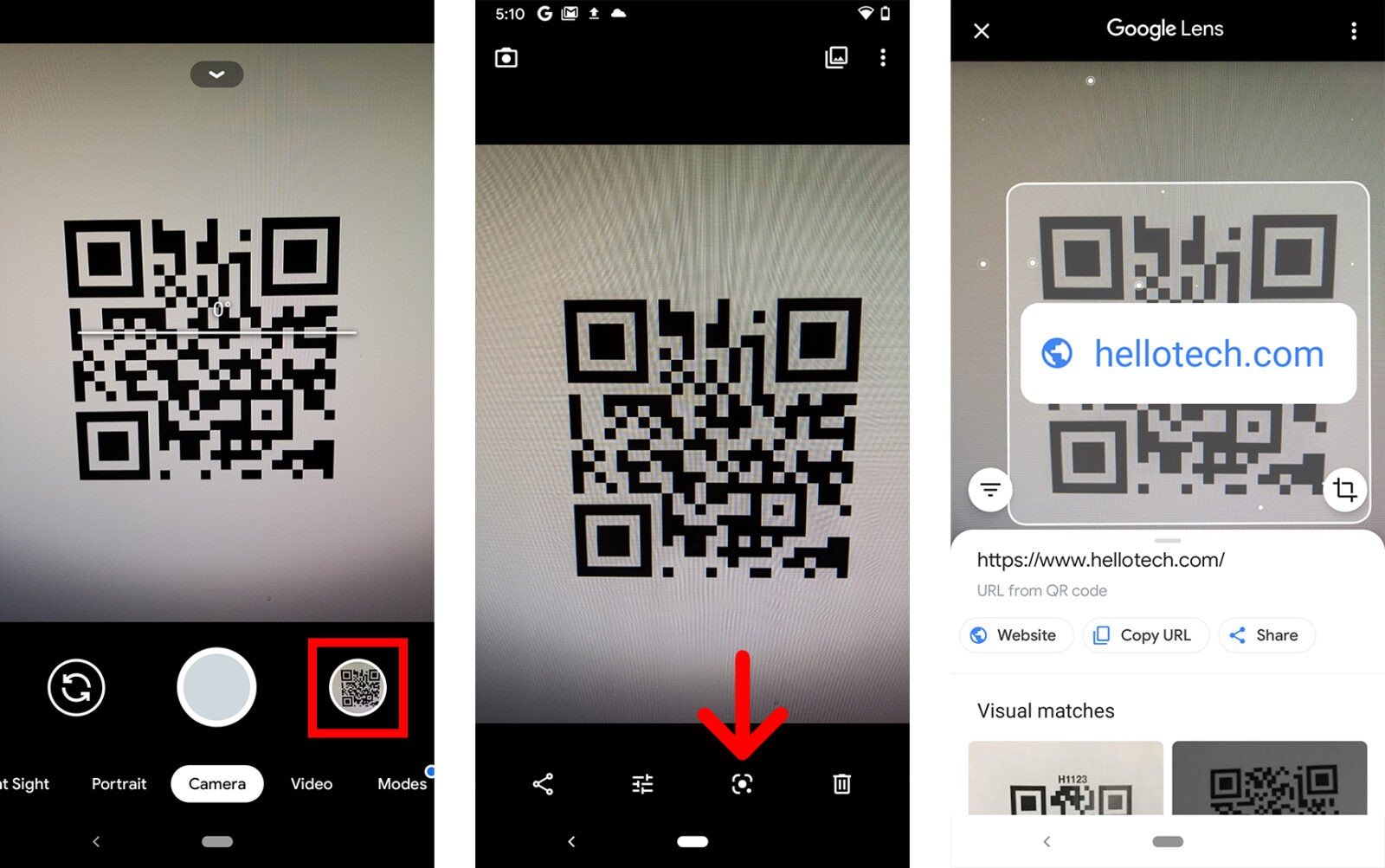
If you don’t see the banner appear, you can use Google Lens instead. You might see the Lens icon (which looks like a circle inside a broken box) somewhere on your screen. Or you might have to tap Modes (or More) in the bottom-right corner of the app and select Lens. Then place the QR code in the white lines and tap the magnifying glass icon to scan it.
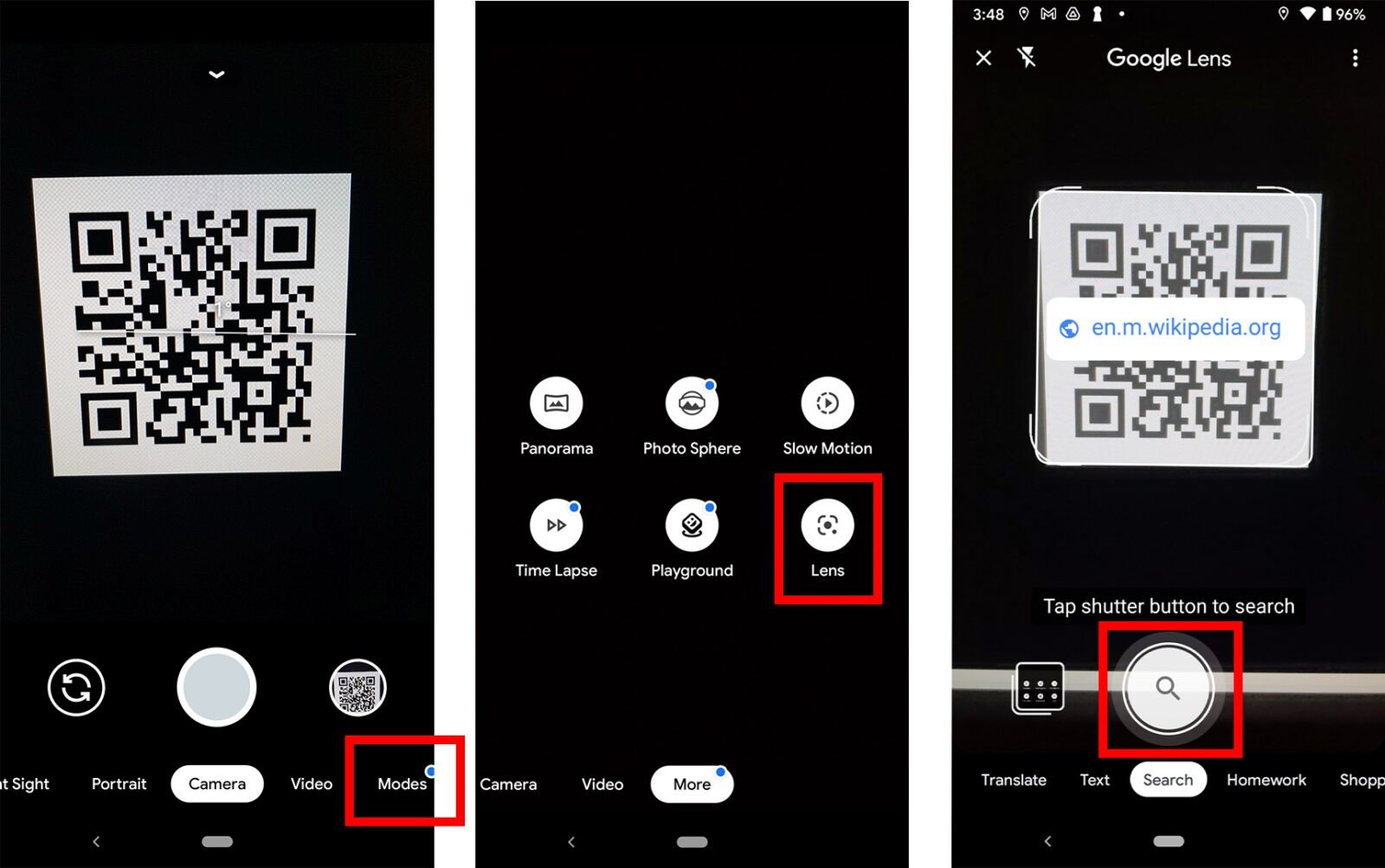
You can also open Lens on some phones by tapping and holding the QR code on your screen until you see a multi-colored spinning wheel. Then tap the pop-up banner when it appears above the QR code.
If Google Lens isn’t working in your camera app, you might have to enable it in your settings. You can check your camera settings in the app or in the general settings on your Android. Then enable the Google Lens suggestions option.
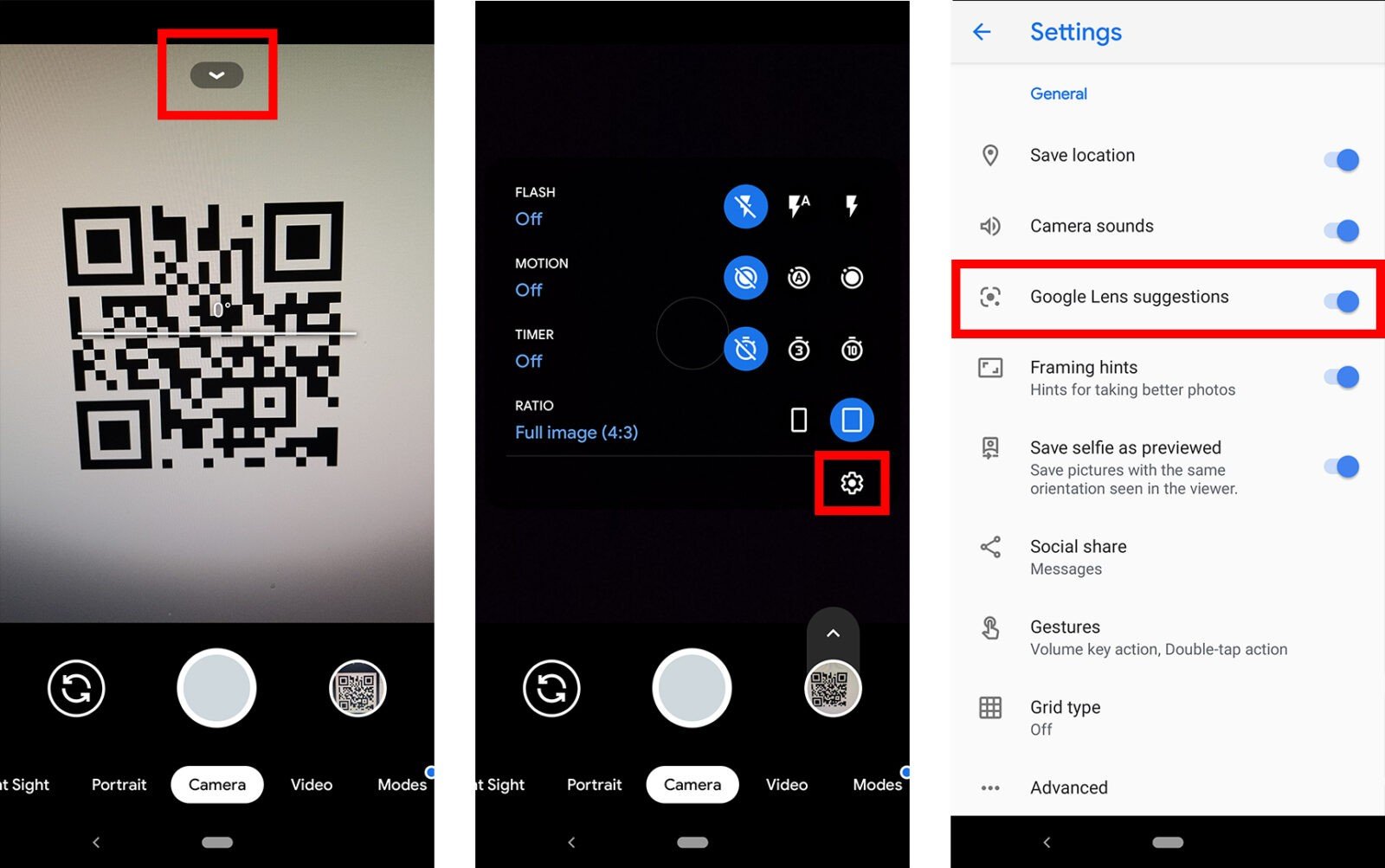
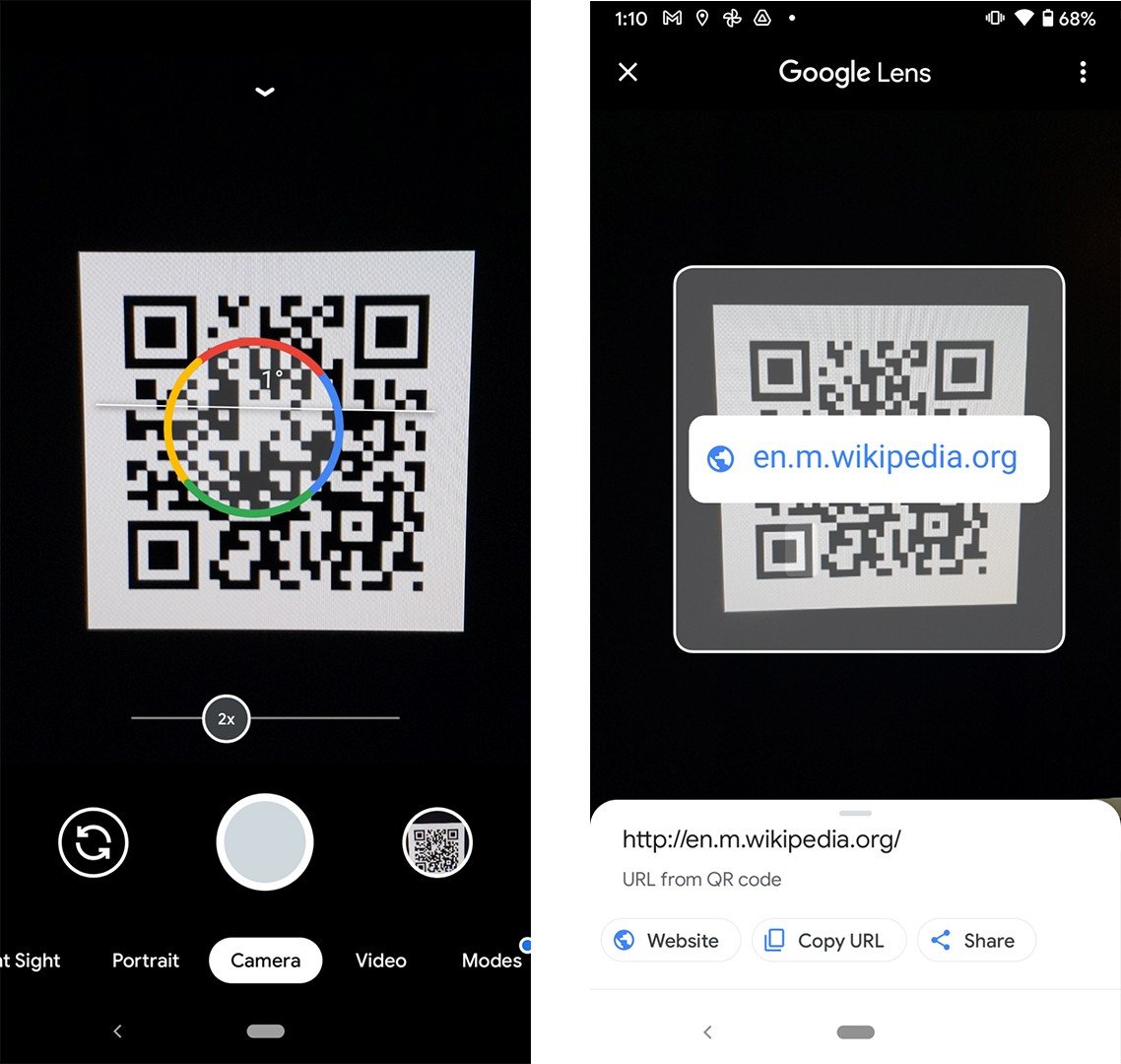
You can also download the Google Lens app from the Google Play Store. Once you open the app, move the QR code to the center of the viewfinder and tap the magnifying glass icon at the bottom of your screen to scan it.
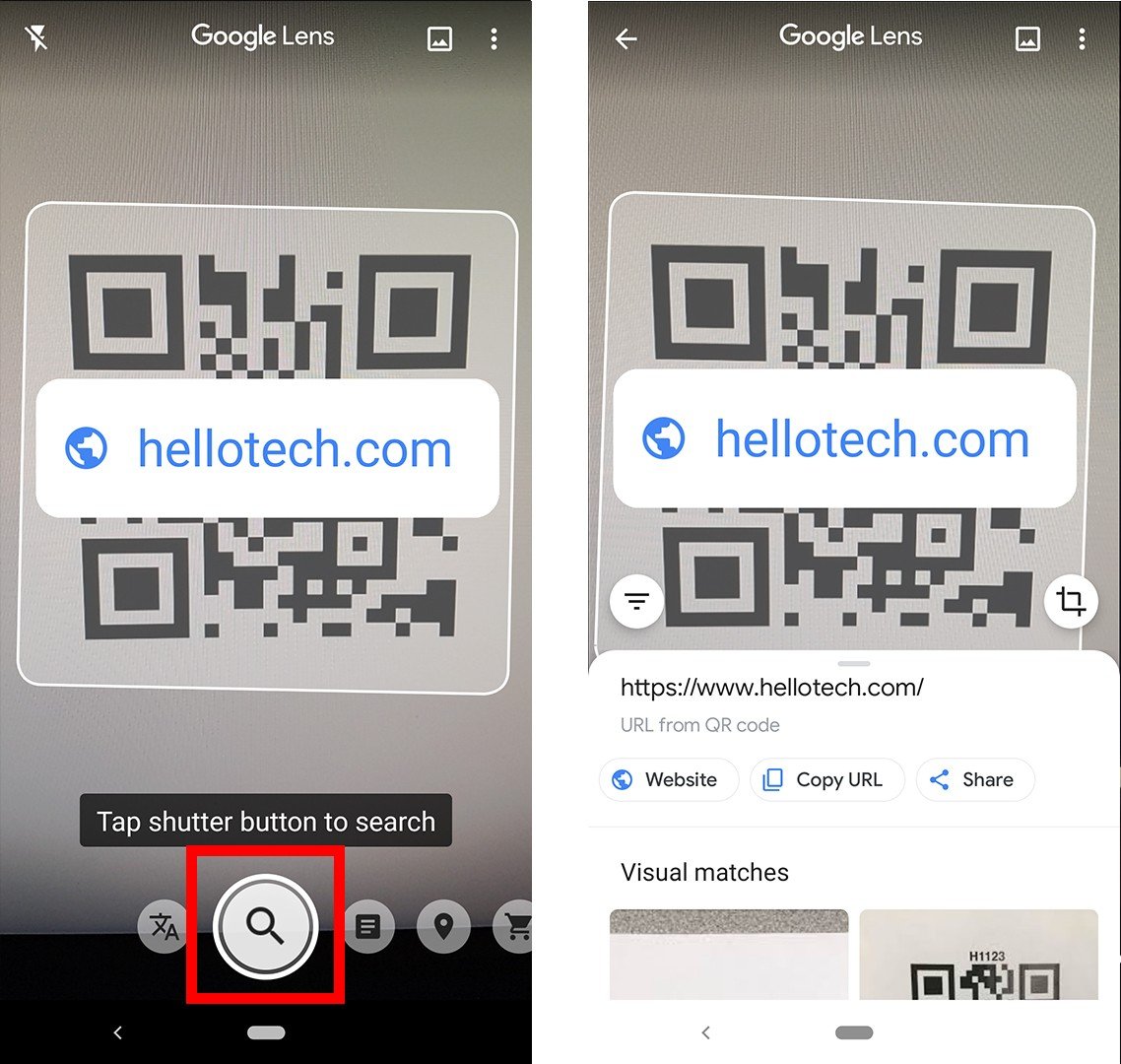
If you are running Android 7 or earlier, your phone might not be compatible with the app, but you might already have the Google Lens feature on your Android device. To find out, press the Home button at the bottom of your device (or the line at the bottom of your screen) until the Google Assistant pops up. Then tap the Google Lens icon or select the microphone icons and say, “open Google Lens.”
If all else fails, you can take a picture or screenshot of the QR code, open the Google Photos app, and tap the Google Lens icon below that picture.
If you want to know how to take a screenshot on your Android phone, check out our step-by-step guide here.
EU Digital COVID Certificate
 |
| been vaccinated against COVID-19 | |
| received a negative test result or | |
| recovered from COVID-19 |
Key features of the certificate
- Digital and/or paper format
- with QR code
- free of charge
- in national language and English
- safe and secure
- valid in all EU countries
Who can get the EU Digital COVID certificate?
- All EU citizens and their family members
- Non-EU nationals who are legally staying or residing in a Member State and have the right to travel to other Member States
Can children get an EU Digital COVID Certificate?
Yes, children can get an EU Digital COVID Certificate.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has given its green light to the use of the BioNTech Pfizer vaccine Comirnaty and the Moderna vaccine Spikevax for children of 12-17 years. Children can also receive a test or recovery certificate. These certificates could also be received by their parents and stored in the parents’ smartphone app.
EU Member States also agreed that minors travelling with parents should be exempt from quarantine when the parents do not need to undergo quarantine, for example due to vaccination. Children under 12 should also be exempt from travel-related testing.
How can citizens get the certificate?
National authorities are in charge of issuing the certificate. It could, for example, be issued by test centres or health authorities, or directly via an eHealth portal.
- Vaccination certificates are issued by the Member State where the vaccination has been administered.
- Test certificates are issued by the Member State where the test has taken place.
- Recovery certificates are issued by the Member State where the recovered person is located.
Information on how to get the certificate should be provided by the national health authorities.
The digital version can be stored on a mobile device. Citizens can also request a paper version. Both will have a QR code that contains essential information, as well as a digital signature to make sure the certificate is authentic.
Member States have agreed on a common design that can be used for the electronic and paper versions to facilitate the recognition.
Select your country on the interactive map below to learn how to get the certificate from your national health authority.
How does it help free movement?
The EU Digital COVID Certificate is accepted in all EU Member States. It helps ensuring that restrictions currently in place can be lifted in a coordinated manner.
When travelling, the EU Digital COVID Certificate holder should in principle be exempt from free movement restrictions: Member States should refrain from imposing additional travel restrictions on the holders of an EU Digital COVID Certificate, unless they are necessary and proportionate to safeguard public health.
In such a case – for instance as a reaction to new variants of concern – that Member State would have to notify the Commission and all other Member States and justify this decision.
How does the certificate work?
| The EU Digital COVID Certificate contains a QR code with a digital signature to protect it against falsification. | |
| When the certificate is checked, the QR code is scanned and the signature verified. | |
| Each issuing body (e.g. a hospital, a test centre, a health authority) has its own digital signature key. All of these are stored in a secure database in each country. | |
 |
 Instantly checks the scanned link is safe
Instantly checks the scanned link is safe Scans codes to open texts, images & more
Scans codes to open texts, images & more Stores results of all your scans
Stores results of all your scans



